Hybrid CMS: FAQ
Advantages of hybrid CMSs & API-based CMSs
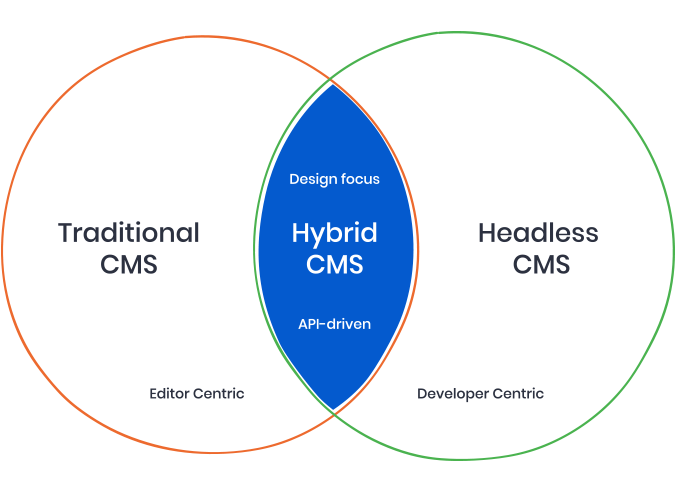
Definition of a hybrid CMS
A hybrid CMS is one combining the features of a conventional CMS with a ‘headless’ CMS.
Advantages of a headless CMS
Like a headless CMS, a hybrid CMS gives you complete freedom to send content in any format to any destination.
Unlike a headless CMS, a hybrid CMS also makes website building and management easy.
Hybrid CMS examples
Eidosmedia’s Cobalt platform is an example of an API-based CMS designed to manage and deliver large volumes of content in the media, corporate and public sectors.
What can you do with a hybrid CMS?
You can use an API based CMS as a digital delivery platform to manage a common content base and then send it out automatically formatted for a vast range of destinations from web portals to mobile apps, social media and voice interactive. It represents the most flexible answer to creating a CMS for banks.
What is ‘Orchestration’ in content management?
‘Orchestration’ refers to the coordination between the various authors, editors and media people who take part in the process of creating a report, a news item, a website or a mobile app. It is the main feature of workflow orchestration platforms used in sectors such as the life sciences.
What functions should content orchestration software offer?
There should be a planning space, visible to all participants, where tasks can be assigned, materials shared and progress monitored.
How should participants access the orchestration application?
There should be close integration between editing and media workspaces and the orchestration space. Mobile user apps allow orchestration of projects involving participants at multiple locations. Find out more about extensibility software.
What is digital asset management (DAM)?
A digital asset management application allows media files of multiple formats to be taken in, tagged with metadata, and stored for later use in media or publishing operations.
What is metadata tagging?
Metadata tagging is a set of labels attached to a digital asset. It may improve the ‘findability’ of the asset (especially if it’s a non-text object like an image or video). It may also aid the processing of the asset by limiting access, and guiding or preventing publication.
- Read the case study:
Intelligent Article Auto-tagging System
Where does an asset management system store its assets?
A powerful DAM system should be able to provide access to multiple repositories, from local files to archives, online libraries and legacy systems. Users should be able to use a single search interface to access all asset sources.